Overview:
- These types of counters fall under the category of synchronous controller counter.
- Here the mode control input is used to decide whether which sequence will be generated by the counter.
- In this case, mode control input is used to decide whether the counter will perform up counting or down counting.
- Designing of such a counter is the same as designing a synchronous counter but the extra combinational logic for mode control input is required.
Steps to design Synchronous 3 bit Up/Down Counter :
1. Decide the number and type of FF –
- Here we are performing 3 bit or mod-8 Up or Down counting, so 3 Flip Flops are required, which can count up to 23-1 = 7.
- Here T Flip Flop is used.
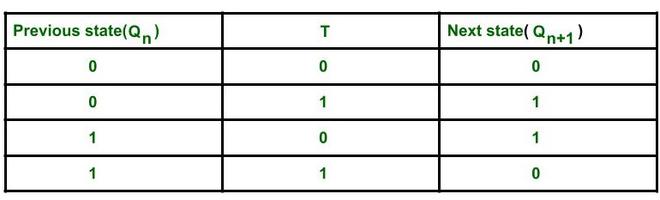
2. Write excitation table of Flip Flop –
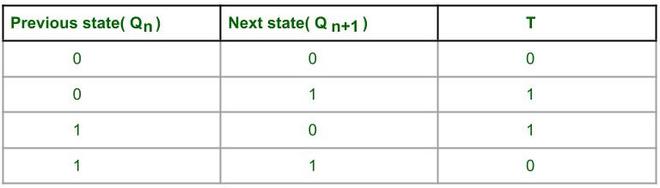
Excitation table of T FF
3. Decision for Mode control input M –
- When M=0 ,then the counter will perform up counting.
- When M=1 ,then the counter will perform down counting.
4. Draw the state transition diagram and circuit excitation table –
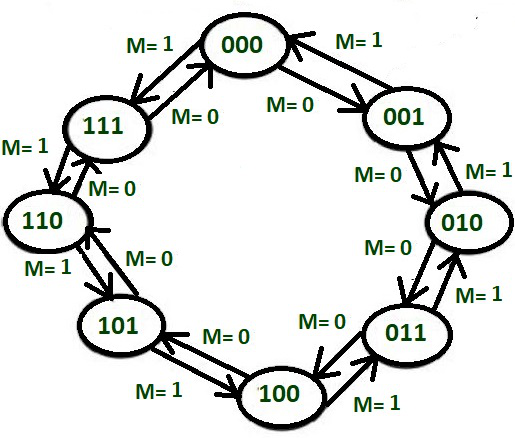
State transition diagram for 3 bit up/down counting.
5. Circuit excitation table –
The circuit excitation table represents the present states of the counting sequence and the next states after the clock pulse is applied and input T of the flip-flops. By seeing the transition between the present state and the next state, we can find the input values of 3 Flip Flops using the Flip Flops excitation table. The table is designed according to the required counting sequence.
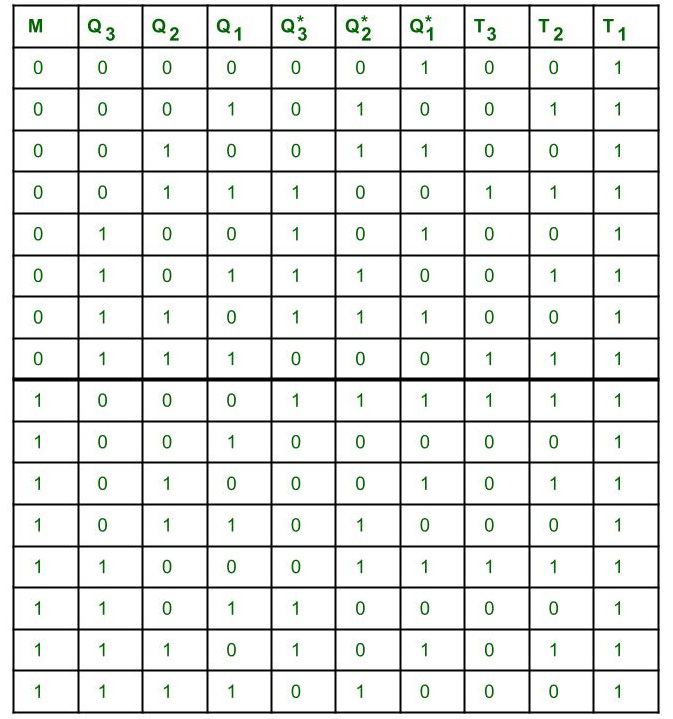
Circuit excitation table
If there is a change in the output state of a flip flop (i.e. 0 to 1 or 1 to 0), then the corresponding T value becomes 1 otherwise 0.
6. Find a simplified equation using k map –
Here we are finding the minimal Boolean expression for each Flip Flop input T using k map.
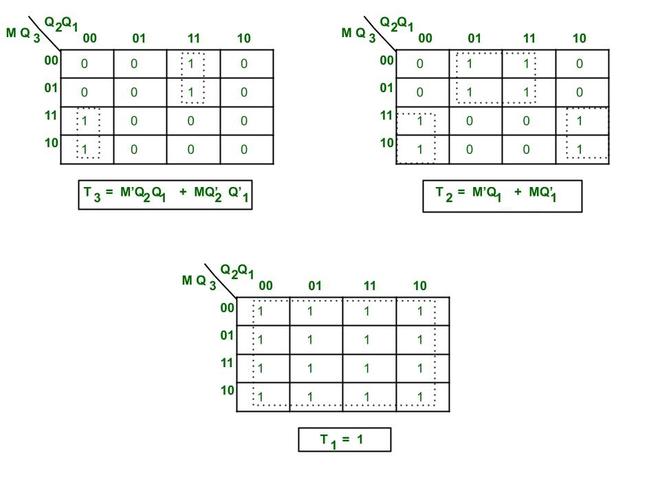
Simplified equation for K map
7. Create a circuit diagram –
The simplified expression for Flip Flops is used to design circuit diagrams. Here all the connections are made according to simplified expressions for Flip Flops.
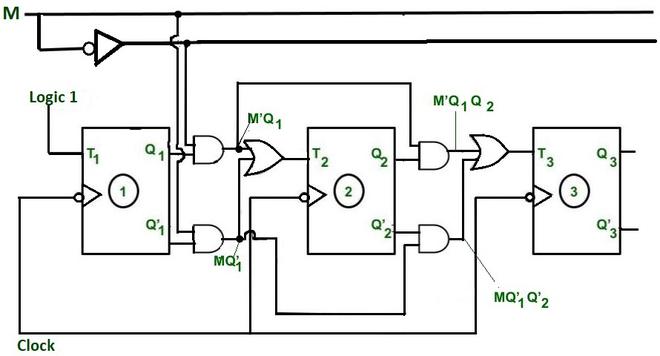
3 bit synchronous up/down counter.
8. Timing Diagram –
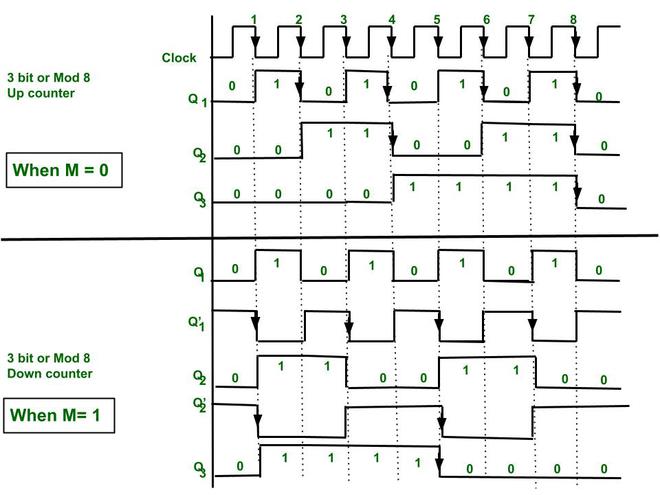
Timing diagram for 3 bit synchronous Up/Down counter
Explanation :
Here -ve edge triggered clock pulse is used for toggling purpose.
Characteristics table of T FF
After every falling edge, when T = 1, the output state of Flip Flop will toggle.
- Initially Q3 = 0 , Q2= 0 , Q1= 0.
Case 1 : When M=0 ,then M’= 1
- T3 = M’Q2Q1 + MQ’2Q’1 = Q2Q1.
- T2 = M’Q1 + MQ’1= 1.Q1= Q1.
- T1= 1.
- Because T1= 1, therefore FF1 output state toggles for every falling edge.
The output state of FF 2 will toggle when Q1 = 1 and the falling edge of the clock pulse occurs.
The output state of FF 3 will toggle only when Q2.Q1= 1 and the falling edge of the clock pulse occurs. - In this way, after every falling edge, state transition takes place and we can get our desired counting sequence.
Case 2 : When M=1 ,then M’ =0
- T3 = M’Q2Q1+MQ’2Q’1 = Q’2Q’1
- T2 = M’Q1+ MQ’1= 1.Q1= Q’1.
- T1= 1.
- Because T1= 1,therefore FF1 output state toggles for every falling edge.
The output state of FF 2 will toggle when Q’1 = 1 and the falling edge of the clock pulse occurs.
The output state of FF 3 will toggle only when Q’2.Q’1= 1 and the falling edge of the clock pulse occurs. - In this way, after every falling edge, state transition takes place and we can get our desired counting sequence.










