Block Diagram of Computer
Mainly computer system consists of three parts, that are central processing unit (CPU), Input Devices, and Output Devices. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is divided into two parts again: arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and the control unit (CU). The set of instruction is in the form of raw data.
A large amount of data is stored in the computer memory with the help of primary and secondary storage devices. The CPU is like the heart/brain of the computer. The user does not get the desired output, without the necessary option taken by the CPU. The Central processing unit (CPU) is responsible for the processing of all the instructions which are given by the user to the computer system.
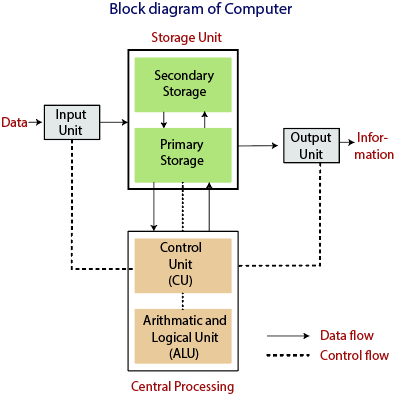
Fig: Block Diagram of the computer.
The data is entered through input devices such as the keyboard, mouse, etc. This set of instruction is processed by the CPU after getting the input by the user, and then the computer system produces the output. The computer can show the output with the help of output devices to the user, such as monitor, printer, etc.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- Storage Unit
- ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
- Control Unit
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The computer system is nothing without the Central processing Unit so, it is also known as the brain or heat of computer. The CPU is an electronic hardware device which can perform different types of operations such as arithmetic and logical operation.
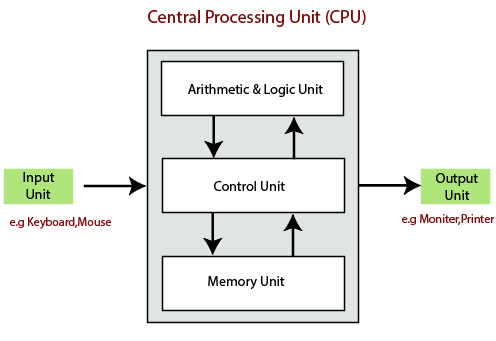
The CPU contains two parts: the arithmetic logic unit and control unit. We have discussed briefly the arithmetic unit, logical unit, and control unit which are given below:
Control Unit
The control unit (CU) controls all the activities or operations which are performed inside the computer system. It receives instructions or information directly from the main memory of the computer.
When the control unit receives an instruction set or information, it converts the instruction set to control signals then; these signals are sent to the central processor for further processing. The control unit understands which operation to execute, accurately, and in which order.
Arithmetic and Logical Unit
The arithmetic and logical unit is the combinational digital electronic circuit that can perform arithmetic operations on integer binary numbers.It presents the arithmetic and logical operation. The outputs of ALU will change asynchronously in response to the input. The basic arithmetic and bitwise logic functions are supported by ALU.
Storage Unit
The information or set of guidelines are stored in the storage unit of the computer system. The storage unit provides the space to store the data or instruction of processed data. The information or data is saved or hold in computer memory or storage device. The data storage is the core function and fundamental of the computer components.
Components of Computer System
The hardware and software exist on the computer. The information which is stored through the device is known as computer software. The hardware components of the computer system are related to electronic and mechanical parts, and the software component is related to data and computer programs. Many elements are connected to the main circuit board of the computer system called a "motherboard."
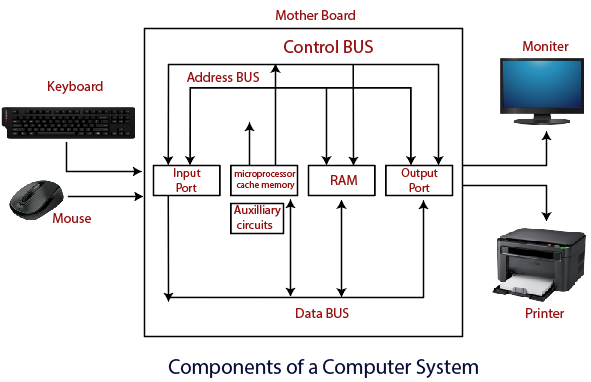
- Processor.
- Main Memory.
- Secondary Memory.
- Input Devices.
- Output Devices.
These are mainly five components of the computer system. The computer hardware, computer software, and liveware exist in the element of the computer system.
Processor
The processor is an electric circuitry within the computer system. The Central processing unit is the central processor or main processor of the computer system. The processor carries out the instructions of the computer program with the help of basic arithmetic and logic, input/output operations.
Main Memory
The Random Access Memory is the main memory of the computer system, which is known as RAM. The main memory can store the operating system software, application software, and other information. The Ram is one of the fastest memory, and it allows the data to be readable and writeable.
Secondary memory
We can store the data and programs on a long-term basis in the secondary memory. The hard disks and the optical disks are the common secondary devices. It is slow and cheap memory as compare to primary memory. This memory is not connected to the processor directly.
It has a large capacity to store the data. The hard disk has a capacity of 500 gigabytes. The data and programs on the hard disk are organized into files, and the file is the collection of data on the disk. The secondary storage is direct access by the CPU; that's why it is different from the primary storage.
The hard disk is about 100 times the capacity of the main memory. The main difference between primary and secondary storage is speed and capacity. There are several large blocks of data which are copied from the hard disk into the main memory.
Input Devices
The user provides the set of instruction or information to the computer system with the help of input devices such as the keyboard, mouse, scanner, etc. The data representation to the computer system is in the form of binary language after that the processor processes the converted data. The input unit implements the data which is instructed by the user to the system.
We can enter the data from the outside world into the primary storage as the input through input devices. The input devices are the medium of communication between the outside world and the computer system.
There are some important features of input devices which are given below:
- The input devices receive or accept the data or instruction from the user, who exist in the outside world.
- These devices convert the data or instruction into the machine-readable form for further processing.
- The input device performs like the connection between the outside world and our computer system.
- The keyboard and mouse are common examples of input devices.
- When the whole procedure is finished, we get the desired output from the output devices such as monitor, printer, etc.
Output Devices
The output devices produce or generate the desired result according to our input, such as a printer, monitor, etc. These devices convert the data into a human-readable form from binary code.
The computer system is linked or connected to the outside world with the help of output devices. The primary examples of output devices are a printer, projector, etc.
These devices have various features which are given below:
- These devices receive or accept the data in the binary form.
- The output devices convert the binary code into the human-readable form.
- These devices produce the converted result and show to the user.
The Central Processing Unit is known as the central processor or main processor. The CPU is an electronic circuitry within the computer which can control the input/ output operations and carries out the instructions of the computer program by the basic arithmetic and logical unit.
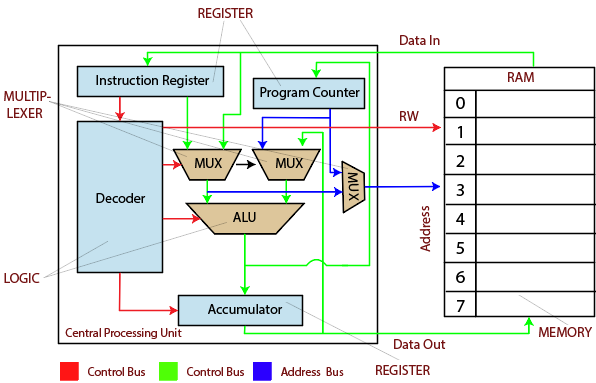
The CPU can control the instructions and data flow. The CPU contains internal memory units which are known as registers. The registers contain data, instructions, counters, and addresses. Some computers have two or more processors. The Central processing unit has two components which are given below:
The Arithmetical Logical Unit (ALU)
The arithmetical logical unit is the combinational digital electronic circuit. It can perform arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. The ALU is the fundamental building block of many types of computing circuits. The ALU (Arithmetic Logical Unit) has the status of inputs, outputs, or both which convey the information about the previous operation or the current operation. The ALU has three parallel data buses consist of two input operand (A and B) and the resulting output. Every data bus is the group of signals that transfer one binary integer number.
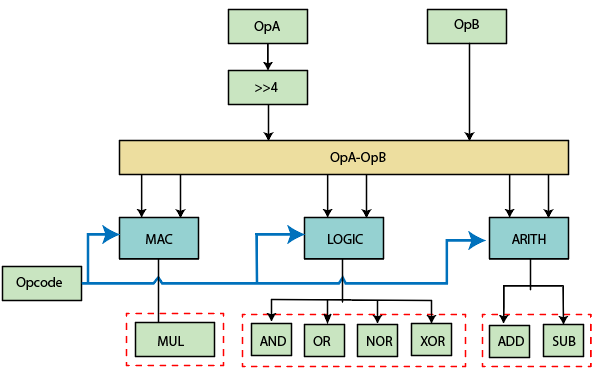
The single CPU (control processing unit), FPU (floating-point unit), and GPU (graphics processing unit) contain multiple ALU’s (logical arithmetic units). The ALU has a variety of inputs and outputs which are electrical conductors.
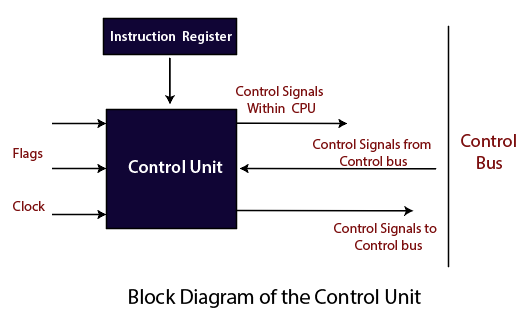
The Control Unit (CU)
The control unit is the component of the central processing unit in the computer system. It is used to control the operation of the processor. The control unit tells to computer memory that how to respond to instructions which are sent to the processor.
The Memory Management Unit (MMU)
The memory management unit is the computer hardware unit having the reference of all memories passed through it. This memory unit is used to the translation of virtual memory address to a physical address. The memory management units allowed to managing the multiple programs in single physical memory with its own address space. It is used to provide virtual addressing.
This translation process is known as memory mapping because addresses are mapped from the logical space into physical space. The memory management unit is not common in embedded systems because the virtual memory requires the secondary storage device such as a disk.
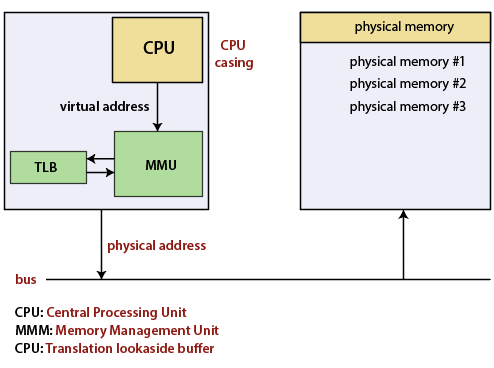
The MMU performs virtual memory management and handling memory protection at the same time. It is located within the computer’s central processing unit, and Sometimes it operates in the separate integrated chip (IC).
The memory management unit accepts the logical addresses from the central processing unit. These logical addresses refer to the program’s abstract address space but do not compare to the actual RAM location. If we add the secondary storage unit such as disk, we can eliminate the parts of the program from the main memory. In the virtual memory system, the memory management unit keeps track of which logical addresses are resident in the main memory. When the CPU requests to the address and that address is not present in the main memory, then the Memory management unit generates an exception which is known as a page fault.
Address Generation Unit (AGU)
The address generation unit or address computation unit is the execution unit inside the central processing unit. This unit can calculate the address used by the CPU to access the main memory. The CPU needs to calculate memory addresses required for fetching the data from memory while performing different operations.
The Capabilities of any AGU is depended on the particular CPU and its architecture. Some CPU architecture includes multiple AGUs that’s why they can execute more than one address- calculation operation, simultaneously.
Some AGUs implement and expose the address calculation operation. The offset address and the reverse carry address operate in parallel and share common input in the AGU (address generation unit).The only difference between the offset address and the reverse carry address is that the carry propagates in the opposite direction. Every ALU address can update one address register from its respective address register file during one instruction cycle. The value of modifier is decoded in ALU address.
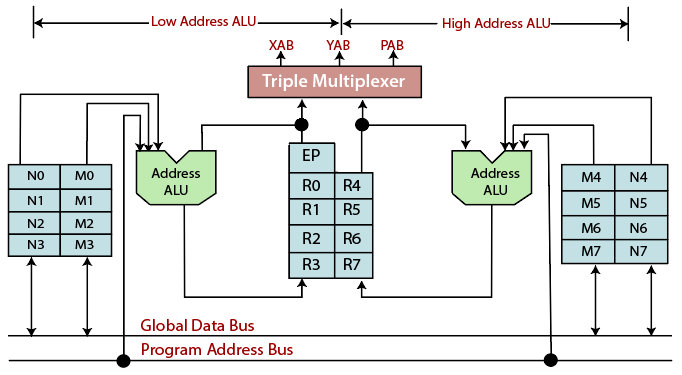
The AGU operates parallel with the other chip resources, to minimize the address generation over the head. The address generation unit implements four kinds of arithmetic operations which are given below:
- Linear operation.
- modulo operation.
- Multiple wraps around modulo.
- Reverse-carry operation.
Cache
The cache is the hardware or software component in the computer memory. The cache memory can store the data so that the future request of that data can be served faster than other memories. The information which is stored in the cache memory might be the result of the earlier computation or the copy of that data, stored elsewhere.
When the system writes data in the cache, it must at some points write that data in the backing store. The cache is made up from the pool of entries. Every entry has associated information, which is the copy of the same data in some backing store.
Each entry also has the tag which specifies the identity of the data in the backing store. When the cache is checked and not found contain any entry with the desired tag, is known as the cache miss. Once the requested data is retrieved, that data is copied into the cache memory and ready for the next access.
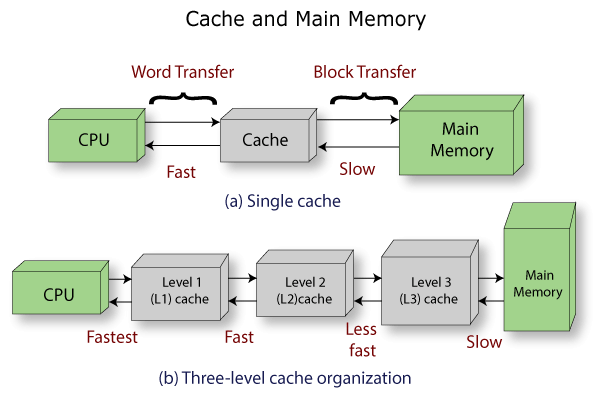
The cache is the small-sized, volatile type of computer memory. It can store frequently used computer programs, application, and data. The cache is integrated on to the motherboard and directly embedded in the processor or main random access memory (RAM).
The Logical cache can stores data in virtual address space. The logical cache is situated in between the processor and memory management unit. The processor can access the data from the logical cache directly without going through the memory management unit. The logical cache is also called the virtual cache.










